文章目录
RequestMappingHandlerMapping 介绍
RequestMappingHandlerMapping是SpringMVC中的一个重要组件,作用是扫描@Controller、@RequestMapping注解修饰的类,然后生成请求与方法的对应关系,当有一个 HTTP 请求进入 SpringMVC 时,就会通过请求找到对应的方法进行执行。
可以简单的想象一下,在RequestMappingHandlerMapping会维护一个Map<String,Handle>,key 存放的是URI,value 存放的是对应处理的handle,例如:
map.put("GET /user",UserController#get)map.put("POST /user",UserController#create)这样通过解析请求就可以很快的找到对应的方法去执行,当然 SpringMVC 的实现肯定不会像上面一样这么简单,不过思路是差不多的。
加载流程
- 流程图
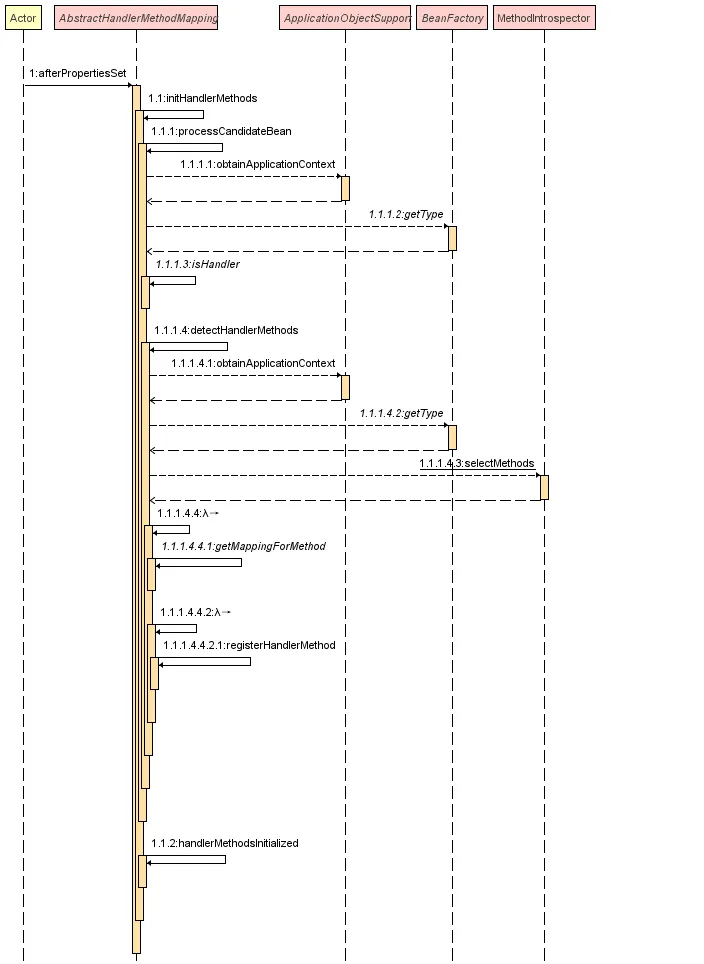
-
RequestMappingHandlerMapping实现了InitializingBean接口,在应用启动时会触发afterPropertiesSet方法。 -
在
initHandlerMethods方法中,会遍历所有候选的 Bean,并通过processCandidateBean方法进行处理。- AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.java
protected void initHandlerMethods() {//遍历所有候选的Bean namefor (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) {if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {//处理Bean nameprocessCandidateBean(beanName);}}handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());} -
在
processCandidateBean方法中,会通过isHandler判断Bean是否为@Controller、@RequestMapping注解修饰的类,是的话调用detectHandlerMethods来检查类中的Handler method -
detectHandlerMethods中会遍历类中所有方法,通过getMappingForMethod方法筛选出@RequestMapping注解修饰的方法,然后解析成method->mapping的 Map 结构存起来,再遍历使用registerHandlerMethod方法注册到 SpringMVC 中- AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.java
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) {Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());if (handlerType != null) {Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);//查询Class中的方法Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> {//通过匿名内部类的方式来进行method的过滤,没有通过@RequestMapping修饰的方法会返回nulltry {return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);}catch (Throwable ex) {throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);}});if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace(formatMappings(userType, methods));}//遍历methods进行注册methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> {Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType);registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);});}}- 通过
registerHandlerMethod将对应的关系存放到mappingRegistry对象中,里面有很多的 Map 用于存储映射关系
- AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.java
//封装HandlerMethod,实际上就是bean name+method,在拦截器中就是暴露的这个对象HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);validateMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping);//将mapping对象和handlerMethod关系存放至mappingLookupthis.mappingLookup.put(mapping, handlerMethod);List<String> directUrls = getDirectUrls(mapping);for (String url : directUrls) {//将非通配符形式的路径与mapping对象关系存放至urlLookupthis.urlLookup.add(url, mapping);}String name = null;if (getNamingStrategy() != null) {name = getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping);addMappingName(name, handlerMethod);}CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping);if (corsConfig != null) {this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig);}this.registry.put(mapping, new MappingRegistration<>(mapping, handlerMethod, directUrls, name));通过源码可以得知,目前有这两个
mappingLookup和urlLookup对象存放了请求映射关系,在请求到来的时候就会通过这两个Map去寻找要执行的方法。
请求流程
先上一张 springMVC 流程图:
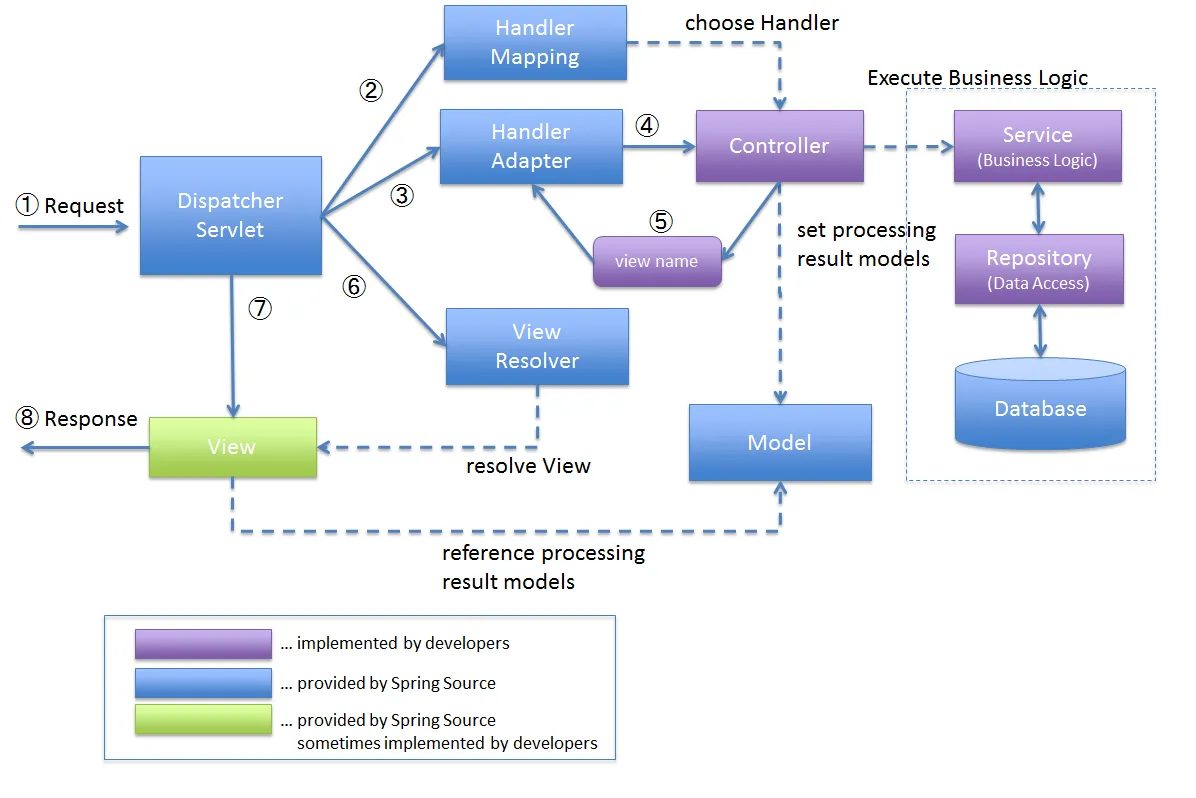
入口由DispatcherServlet统一接管,然后通过上一步生成好的HandlerMapping映射关系来查找请求对应的处理方法。
- DispatcherServlet.java
// 寻找当前请求的处理方法mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);if (mappedHandler == null) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return;}在getHandler方法中就是对应的逻辑了,代码如下:
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { if (this.handlerMappings != null) { //遍历handlerMappings,只要能根据请求匹配到一个handler就返回 for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) { HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request); if (handler != null) { return handler; } } } return null;}这里值得一提的是handlerMappings是一组HandlerMapping接口的实现,SpringMVC默认提供的是org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping,如果有需要我们也可以自定义一个HandlerMapping实现来处理请求。
接着一路跟踪源码,直到AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request)方法,就可以看到具体的实现了。
- AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.java
//先直接使用URI进行匹配,适用于没使用通配符修饰的接口路径,对应urlLookupList<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);if (directPathMatches != null) { //路径匹配到之后,还要根据method、header、consume、produce等等条件继续进行匹配 addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);}if (matches.isEmpty()) { //如果没匹配到,再通过通配符的方式去匹配,对应mappingLookup addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request);}至此与 RequestMappingHandlerMapping 有关的请求流程就已经介绍完了,最后再附上一张类图:
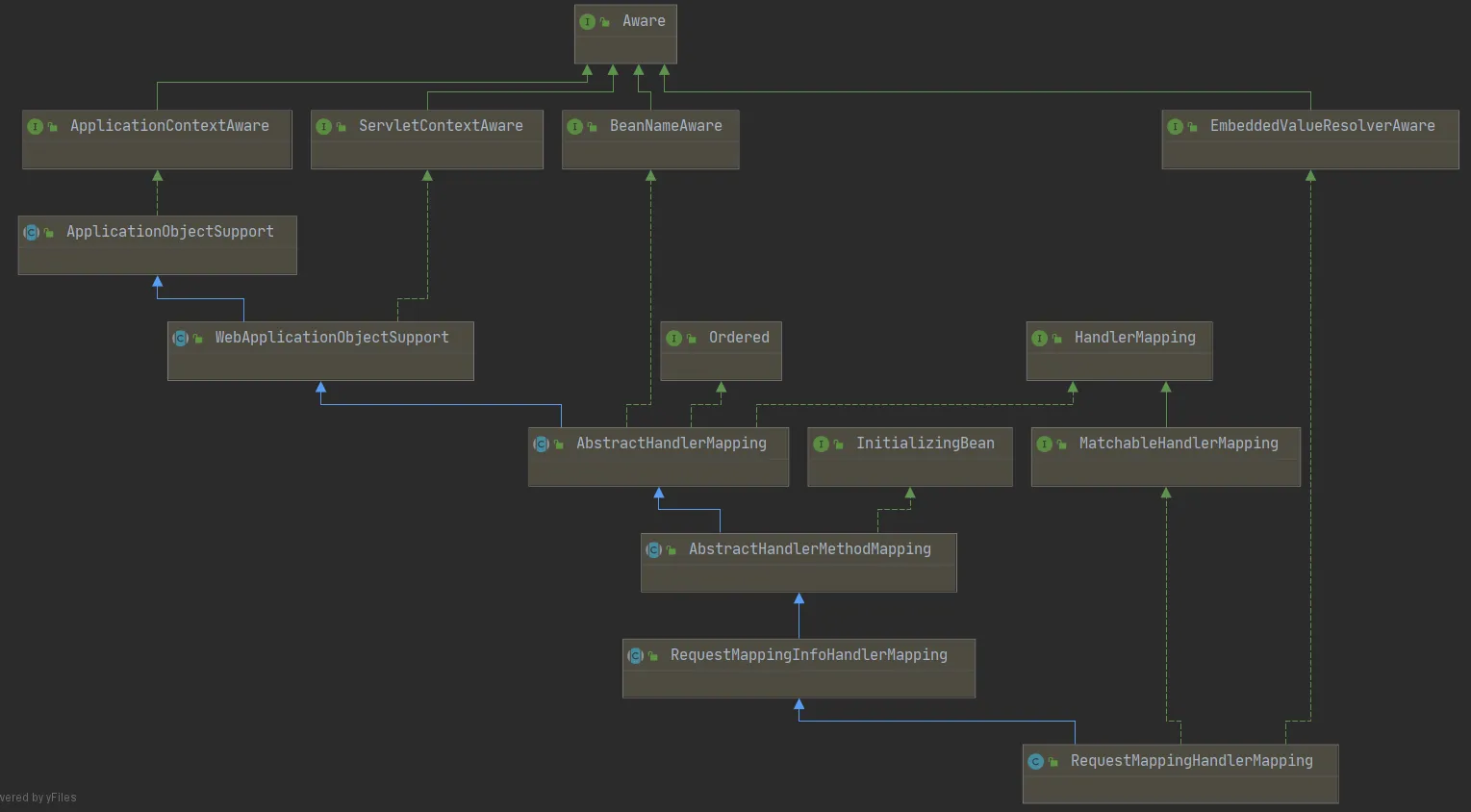
大部分的实现逻辑都在父类AbstractHandlerMethodMapping中。
自定义 RequestMappingHandlerMapping
终于步入主题了,在了解RequestMappingHandlerMapping的大概的原理之后,就很清楚的如何来魔改RequestMappingHandlerMapping。
需求
项目中有一个BaseController基础类,当有新的需求开发时只需要继承该类就会拥有对应的CRUD接口,例如:
- BaseController.java
public class BaseController<T> { @PostMapping public Result<T> insert(@Validated @RequestBody T vo) { //... }
@PutMapping("{id}") public Result<T> update(@PathVariable @NotNull String id, @RequestBody @Validated T vo) { //... }
@DeleteMapping("{id}") public Result<T> delete(@PathVariable @NotNull String id) { //... }
@GetMapping("{id}") public Result<T> get(@PathVariable @NotNull String id) { //... }}- AppController.java
@RestController@RequestMapping("/app")public class AppController extends BaseController<App>{
}这样AppController就拥有了基本的CRUD接口功能,但是在某些情况的时候我需要屏蔽掉某个接口,可以通过重写方法来实现:
- AppController.java
@RestController@RequestMapping("/app")public class AppController extends BaseController<App>{
//屏蔽get接口 @Override @GetMapping("{id}") public Result<T> get(@PathVariable @NotNull String id) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); }}这样实现其实也没啥问题,不过会占用一个路由,如果想重写这个接口,并且返回不同的响应体,就实现不了了,例如:
- 重写父类方法编译不通过,因为泛型不兼容
Result<App>!=Result<AppDetailDTO>
//返回特殊的AppDetailDTO@Override@GetMapping("{id}")public Result<AppDetailDTO> get(@PathVariable @NotNull String id) { //...}- 屏蔽父类接口,并声明一个新的方法来实现
//屏蔽get接口@Override@GetMapping("{id}")public Result<T> get(@PathVariable @NotNull String id) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}
//声明一个新方法来实现@GetMapping("/detail/{id}")public Result<AppDetailDTO> getDetail(@PathVariable @NotNull String id) { //...}通过重新定义一个新的路由来实现,虽然说可以达到目的,但是感觉不够优雅,/{id}路由白白就浪费了,这个时候就只能通过自定义RequestMappingHandlerMapping来实现了。
思路
通过上面的分析可以得知,在应用启动时RequestMappingHandlerMapping会去扫描所有的handle进行关系映射,可不可以实现一个注解,在扫描某个方法时,如果有该注解修饰的时候就跳过。
根据源码可以得知getMappingForMethod,是扫描method的处理入口,方法签名如下:
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType)这个方法可以拿到Method,只有重写该方法并且判断Method上有自定义的注解修饰直接返回 null 就可以达到取消路由注册的目的了。
实现
定义一个@Disable注解,用于标识方法不进行路由注册:
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Documentedpublic @interface Disable {}通过实现WebMvcRegistrations接口来自定义RequestMappingHandlerMapping类,并重写getMappingForMethod方法:
@Configuration@ConditionalOnWebApplicationpublic class WebAutoConfiguration implements WebMvcRegistrations {
@Override public RequestMappingHandlerMapping getRequestMappingHandlerMapping() { return new RequestMappingHandlerMapping() { @Override @Nullable protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) { //如果方法上有@Disable注解,直接返回null if (AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, Disable.class) != null) { return null; } //否则还是按照以前的逻辑进行处理 return super.getMappingForMethod(method, handlerType); } }; }
}这样之前的需求就可以解决了:
//屏蔽get接口@Disable@Override@GetMapping("{id}")public Result<T> get(@PathVariable @NotNull String id) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}
//声明一个新方法来实现,并且路由不变@GetMapping("{id}")public Result<AppDetailDTO> getDetail(@PathVariable @NotNull String id) { //...}父类的方法用@Disable注解修饰了,SpringMVC 并不会加载这个路由,在项目重启的时候就不会报错提示有两个相同的路由存在。
总结
不要为了看源码而看源码,而是带着问题去看框架的源码才是有意义的。
